The Runway of Dreams Celebrates Disability in Fashion
by Erin Hawley
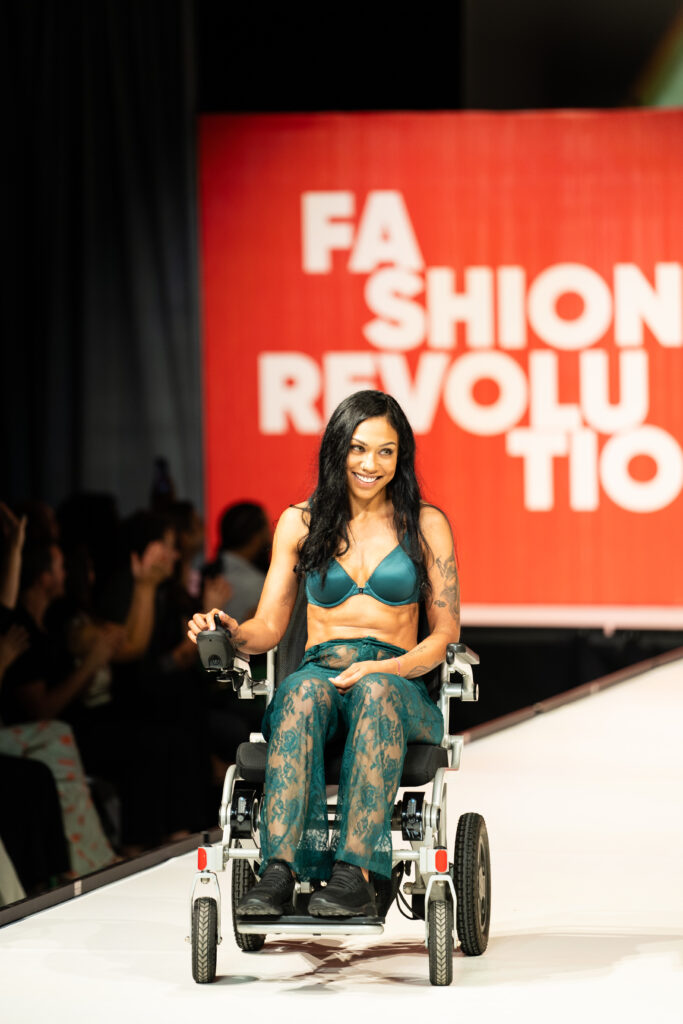
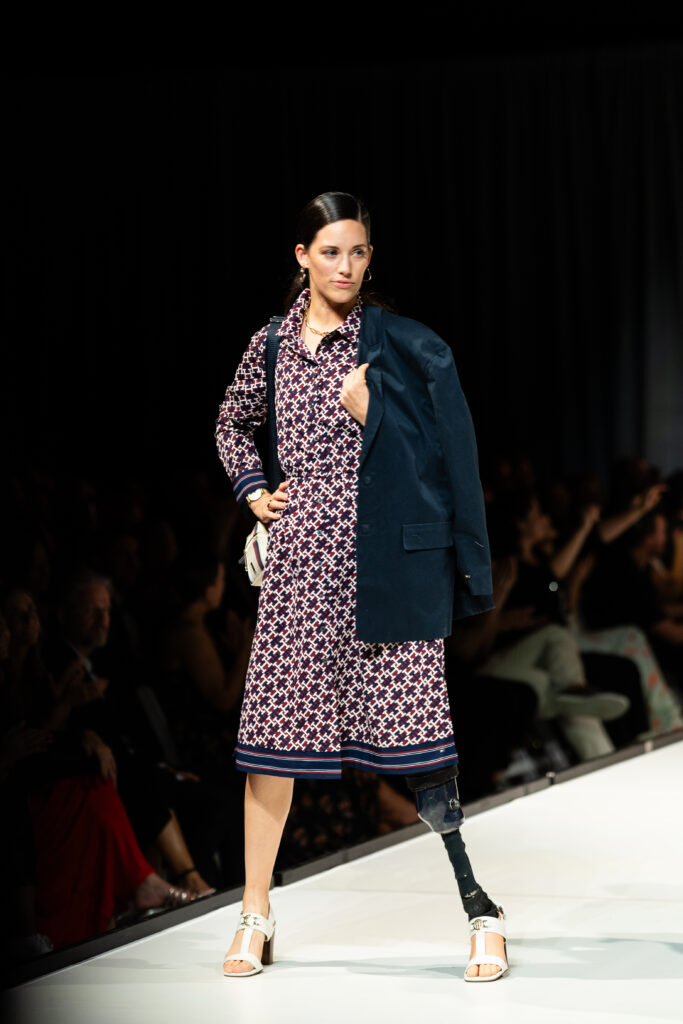
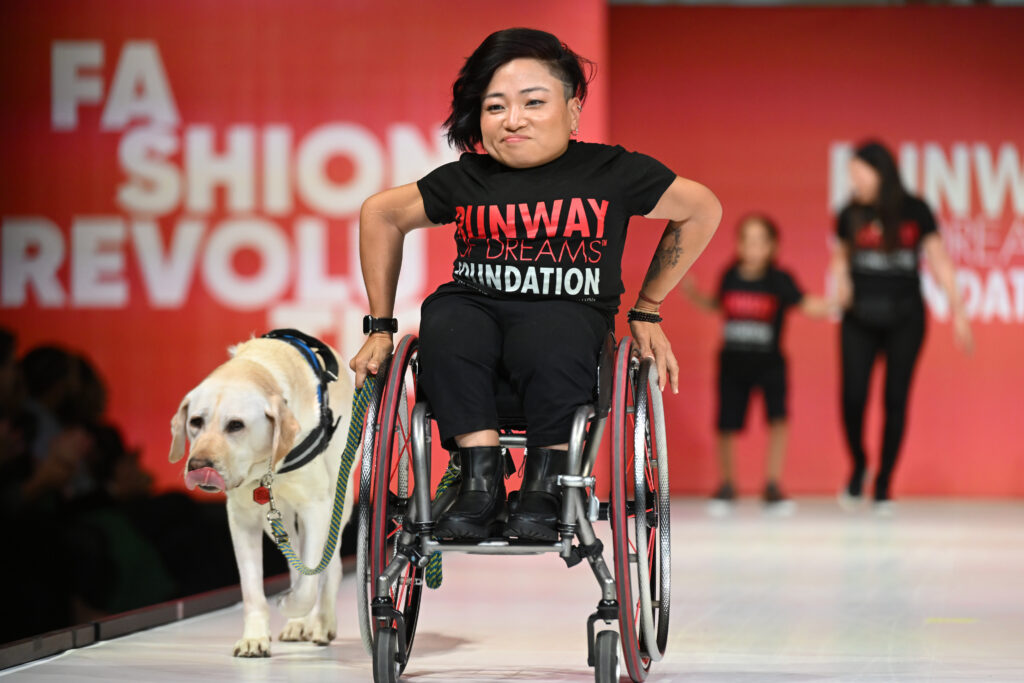
On September 13, Adaptive and accessible fashion was center stage. The Runway of Dreams Foundation, a public charity that empowers people with disabilities through inclusion in fashion and beauty, hosted the event at the Powerhouse Arts building in Brooklyn, NY during the highly popular New York Fashion Week. As an organization that promotes and celebrates innovative design, this year’s theme of A FASHION REVOLUTION called for models with disabilities to come down the runway in the latest apparel and footwear from companies like Tommy Hilfiger, Zappos, Steve Madden, and Target. Victoria’s Secret also unveiled their first-ever Adaptive Intimates line. As with every Runway of Dreams show, every model highlighted the diversity of disability. There were models of different ages, BIPOC models, wheelchair users, cane users, folks with limb differences, little people, models with care assistants, and other presentations of disability.
“Every runway show is better than the last,” says Mindy Scheier, founder of The Runway of Dreams. “The most exciting part of the 2023 A FASHION REVOLUTION was having 11 mainstream brands on our runway, including Victoria’s Secret, who decided that this was the runway to debut their Adaptive Intimates. Having women with disabilities on our runway proudly wearing Adaptive bras and panties that were developed with and for women with disabilities left me awestruck.”
Mindy says conviction is what inspired her to start the charity in 2014, after 20 years working as a fashion designer and stylist. When her then 8-year-old son Oliver, who has Muscular Dystrophy, asked for jeans that he could button himself and wear over his leg braces, she adapted the jeans herself – and then conducted extensive research on how to mainstream and manufacture accessible clothing. In 2016, she partnered with Tommy Hilfiger to create the first-ever mainstream adaptive clothing line on the market.
With an overwhelming response to the collaboration with Tommy Hilfiger, companies have been looking to hire people with disabilities to build their own inclusive and accessible offerings. In 2019, Mindy founded GAMUT Management, a consulting and talent management company that represents people with disabilities across fashion and entertainment.
Mia Ives-Rublee, a client of GAMUT Management and one of the Zappos models in the Runway of Dreams show, also participated in the Easterseals Disability Film Challenge as a film maker and actor. “Being able to see yourself in clothes or on screen shows that you matter as a person; that your story matters,” she says. Mia also mentioned that disabled people are often excluded from media and fashion, even though, according to the CDC, 1 in 4 Americans identify as having a disability: “With that understanding, it is easy to explain to non-disabled people the importance of creating clothing for a variety of body sizes and needs. To understand those needs, disabled people need to be a part of the fashion industry from the designers to the board members. Working together, they can create clothing that is adaptable to wider body types and needs.”
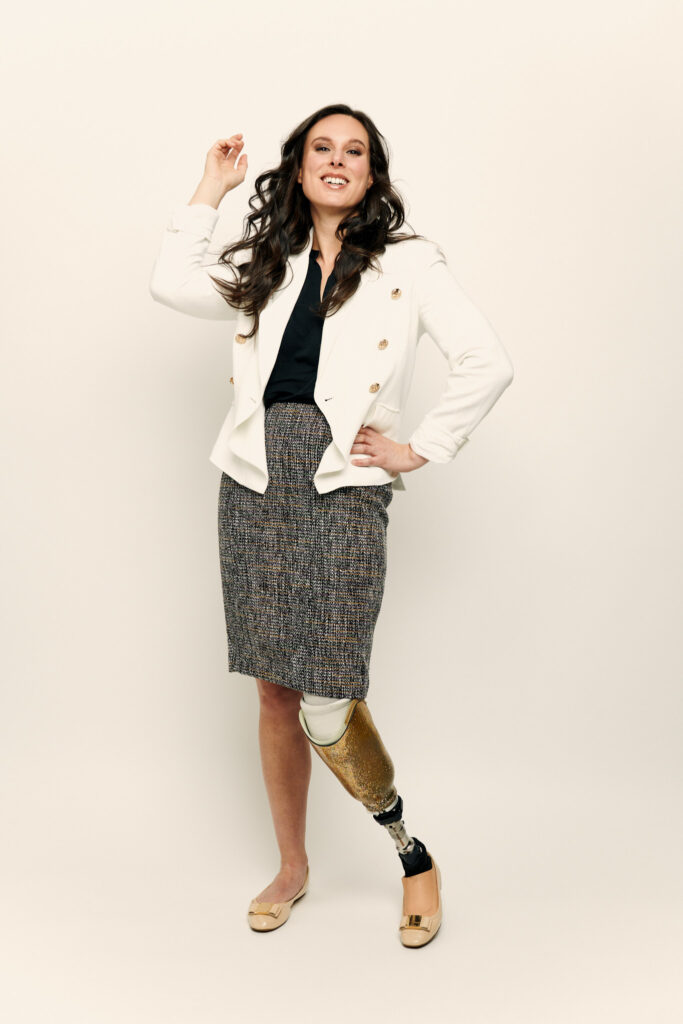
Advocate and model for Runway of Dreams, Caitlin Connor, agrees. “So many people in the disability community are left out of the fashion industry and shopping can be depressing. We need organizations like Runway of Dreams to show brands that we harness both buying and selling power and that disability impacts everyone at some point in life.” Caitlin learned about Runway of Dreams when searching for resources for her nonprofit Be More Adaptive, which is a one-stop resource and community for all things adaptive and accessible. “When I became an amputee through a traumatic accident, my world spiraled with confusion as I searched to understand my new life with a physical disability. While recovering from the accident, I was also pregnant and eventually got laid off from my job. It gave me time to research for as many resources as possible and led to me developing Be More Adaptive.”
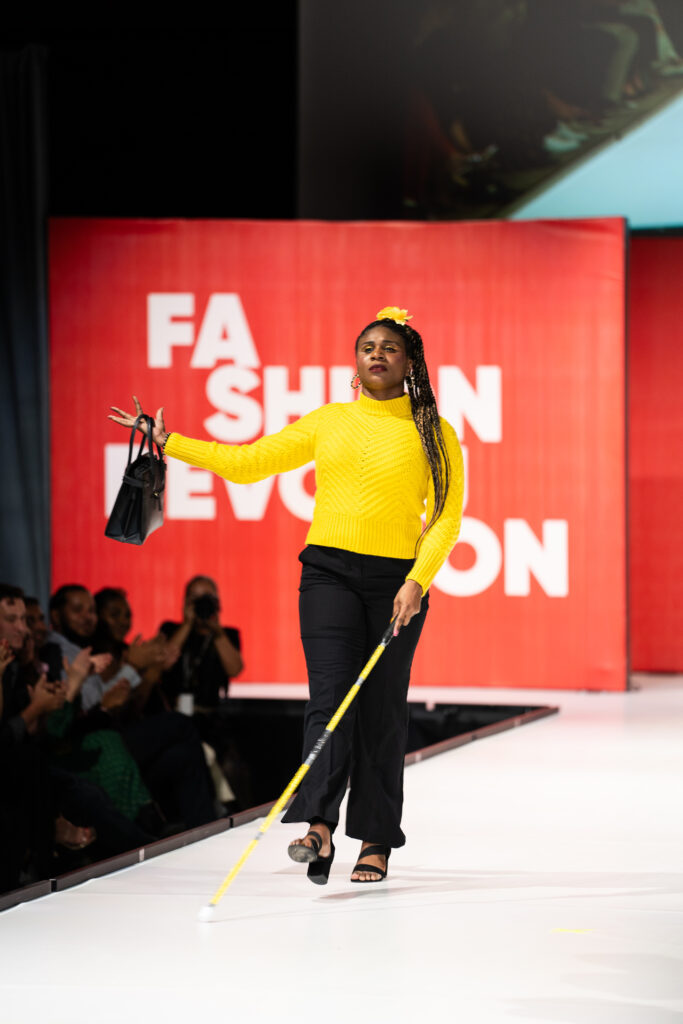
Runway model and music artist, Lachi, shared that we can change the fashion industry “…by supporting models who celebrate their disability as a unique part of their identity, or by spreading awareness to adaptive fashion brands and disabled designers, and by embracing the cutting edge, newness of the disabled body and the untapped stories it tells.”
Lachi is another participant of the Easterseals Disability Film Challenge, with the “Unlucky in Love” short film alongside Imani Barbarin and Rachel Handler. Like the Runway of Dreams show, Lachi says, “the film challenge proves that there are as many opportunities as there are ideas, that we create our own opportunities, and that we need to stop waiting to be discovered and need to start being the discoverers. Both the Runway and the Challenge allow folks with disabilities to cut their teeth in fashion or film and to grow among a supportive community of peers, allies, friends, and collaborators.”
Fashion isn’t just the stylish clothes we wear – fashion is expression, empowerment, and a part of culture. Lachi is a big fan of what she calls “glam canes” – white canes used by people with low vision to navigate and bejeweled with rhinestones from top to bottom. She has a cane to match every outfit. “It’s an instant showstopper, icebreaker, and leaves an impression,” Lachi says. “It also allows me to celebrate my blind identity in a very bold and sophisticated way.”
Self-expression and community are at the core of the Runway of Dreams Foundation. It’s evident in how supportive models are of each other … Evident in the hundreds of people who attend the runway show with enthusiasm and pride… shown through the diversity seen at every event … bringing people with and without disabilities on the same path toward possibility and inclusivity. And, with the efforts of such an incredible community, we are seeing progress in fashion – with much more ahead.